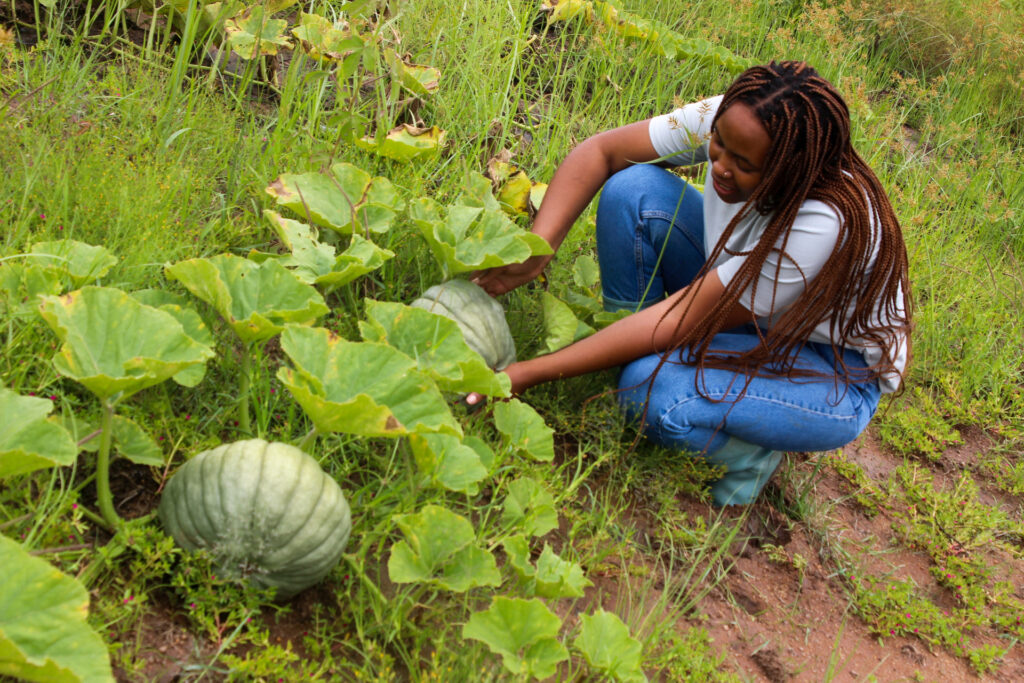


Plants and trees have complex ways of reproducing.
When we think about plants and trees, we mostly focus on their beauty and the shade they provide. But did you know that plants and trees can have sexes, just like animals?
Some plants are male, some are female, and some are even both.
What to know about plant sexes
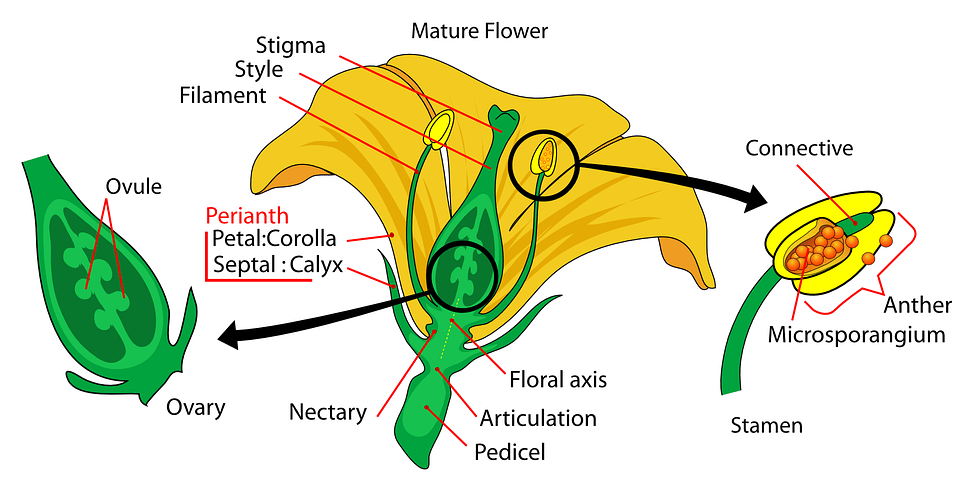
Plants are incredibly diverse when it comes to their reproductive strategies. Most plants have flowers, and these flowers can be male, female, or both. The male parts of a flower are called stamens, which produce pollen.
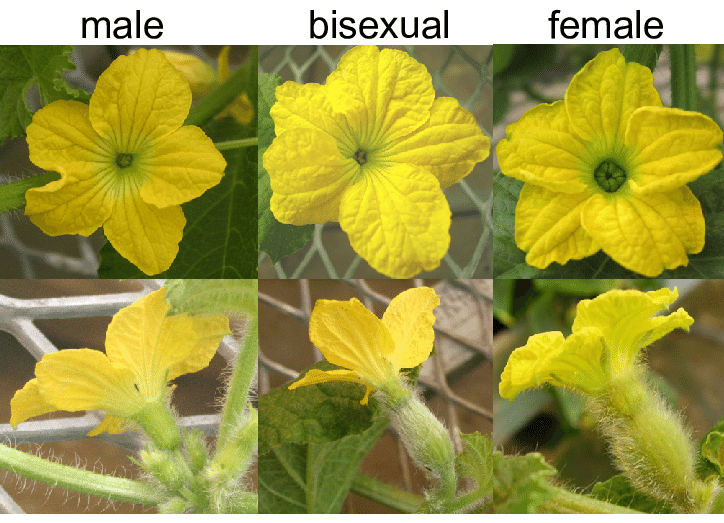
The female parts are called pistils, which contain the ovules. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
- Male flowers: These have stamens but no pistils. They produce pollen.
- Female flowers: These have pistils but no stamens. They can receive pollen to produce seeds.
- Hermaphrodite flowers: These have both stamens and pistils. They can produce and receive pollen.
How plants reproduce
Plants reproduce through a process called pollination. Pollination occurs when pollen from the male part of one flower lands on the female part of another flower. This can happen in several ways:
- Wind pollination: Pollen is carried by the wind from one flower to another.
- Animal pollination: Bees, butterflies, birds, and other animals carry pollen from flower to flower.
- Self-pollination: Some plants can pollinate themselves because they have both male and female parts.
Different types of plant sexes
While many plants have both male and female parts in the same flower, there are different types of plant sexes:
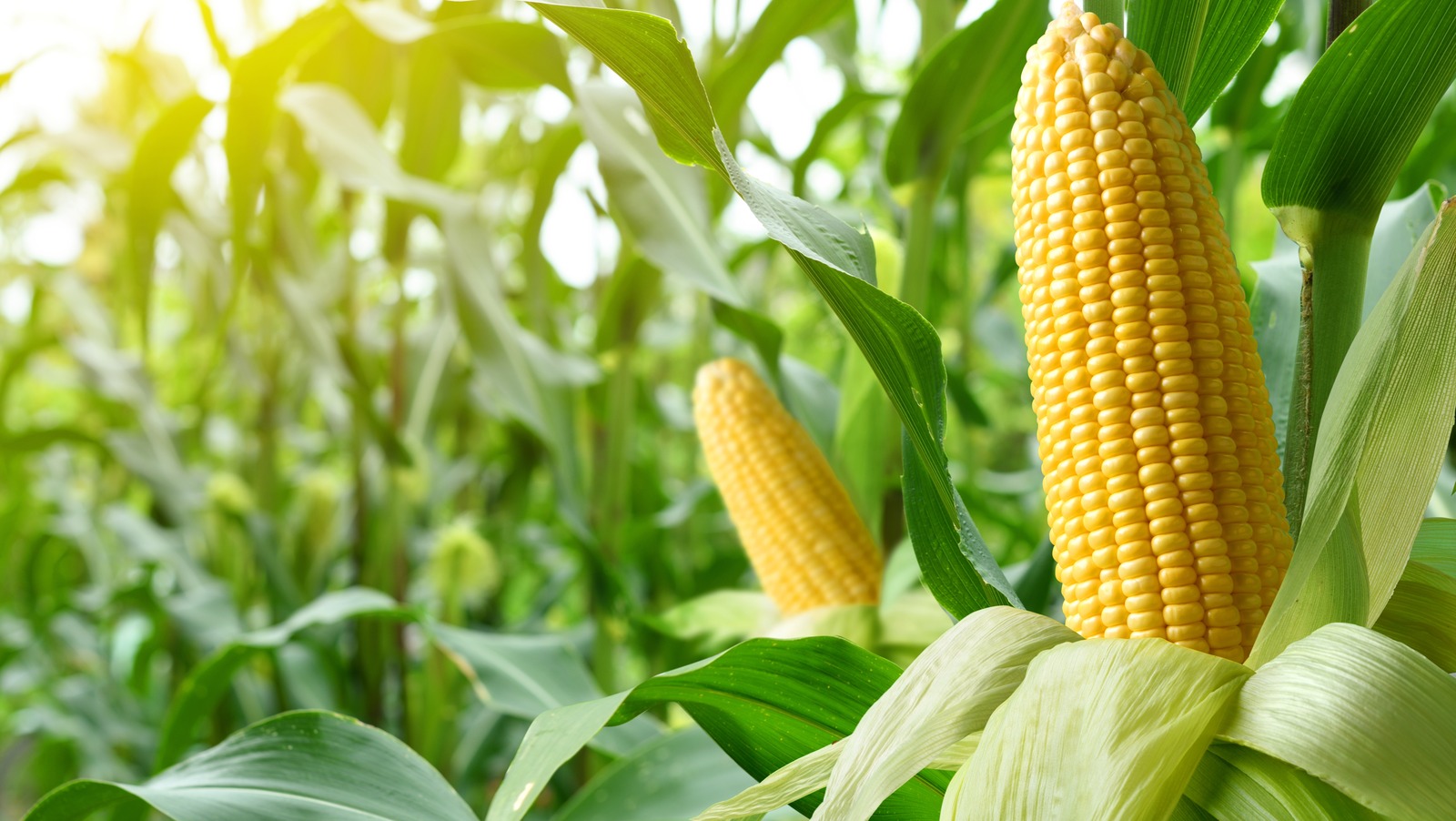
- Monoecious plants: These plants have separate male and female flowers on the same plant. For example, corn is a monoecious plant. It has tassels (male flowers) and ears (female flowers) on the same plant.

- Dioecious plants: These plants have male and female flowers on separate plants. For example, holly plants are dioecious. You need a male and a female plant to get berries.
- Hermaphroditic plants: These plants have flowers that contain both male and female parts. Many fruit trees, like apple trees, are hermaphroditic.
Changing sexes
Interestingly, some plants can change their sex during their lifetime. This is called sequential hermaphroditism. For example, certain species of fig trees can change from male to female or vice versa, depending on their environment and the needs of the population. This flexibility helps ensure that plants can reproduce successfully even if conditions change.
Why plant sexes matter
Understanding plant sexes is important for several reasons:
- Gardening and farming: Knowing the sex of plants helps gardeners and farmers manage crops better. For instance, if you want to grow pumpkins, you need both male and female flowers.

- Conservation: In nature, knowing which plants are male and which are female can help conservationists protect endangered species.
- Scientific research: Studying plant sexes can reveal a lot about genetics, evolution, and how plants adapt to their environments.
ALSO READ: 9 low-maintenance plants to add vibrancy to your home
Plants and trees are not just passive green beings; they have complex and fascinating ways of reproducing.
This content was created with the help of an AI model and verified by the writer.
Read Full Story


















Facebook
Twitter
Pinterest
Instagram
Google+
YouTube
LinkedIn
RSS