
In an increasingly digital world, internet access has become a necessity for work, education, and business in Ghana.
However, the high cost of data remains a significant barrier for many citizens, limiting their ability to fully participate in the digital economy.
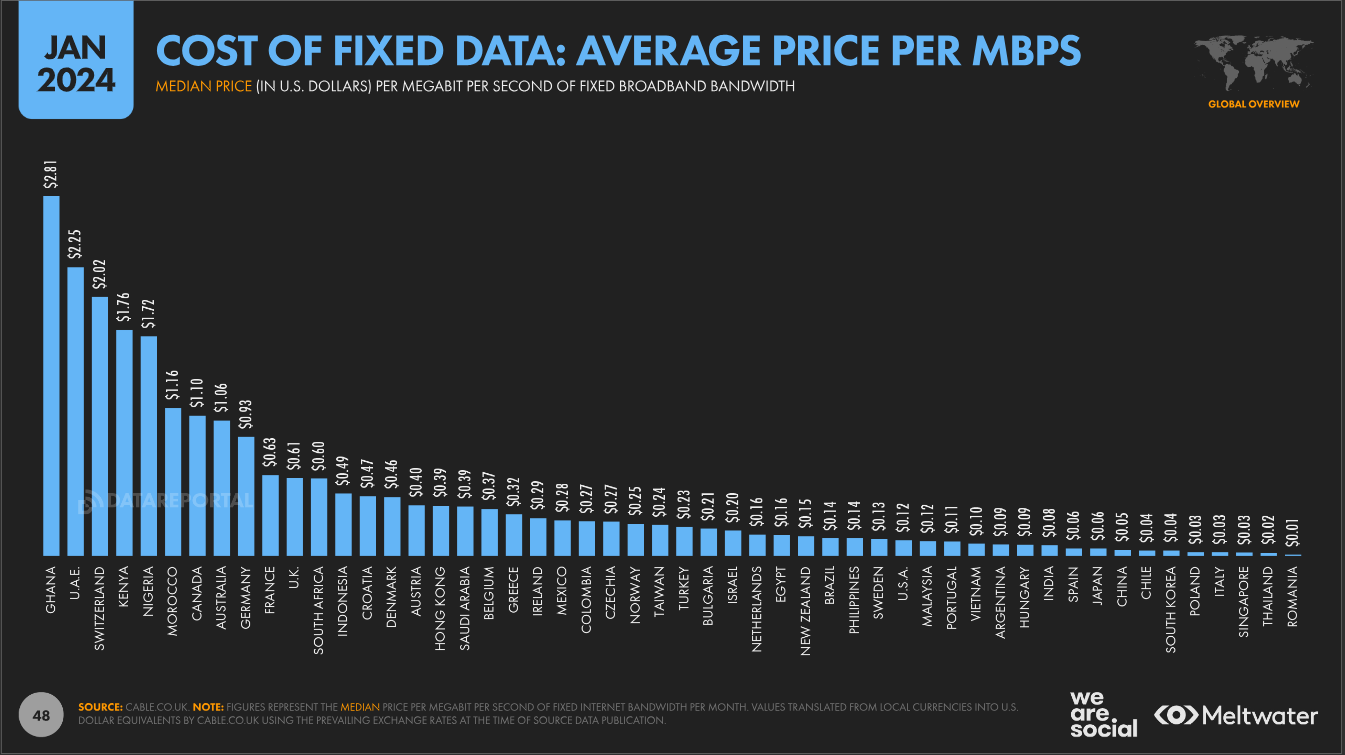
While neighbouring African countries like Kenya and Nigeria have seen notable reductions in data prices, Ghana continues to struggle with expensive internet services.
This raises a critical question: Will Ghanaians see a decrease in internet costs by 2025?
This article delves into the factors driving high data prices in Ghana, including infrastructure expenses, taxes, limited market competition, and exchange rate challenges.
MUST READ: Galamsey: 3 Chinese, 9 Ghanaians arrested for illegal mining in Western Region
It also explores the perspectives of telecom companies, the efforts of regulators, and the strategies Ghanaians are using to cope with high data costs.
Finally, it examines whether the future holds hope for more affordable internet, considering global trends, technological advancements, and growing advocacy for accessible connectivity.
Why are internet costs still high in Ghana?
1. Infrastructure expenses
Telecom providers incur substantial costs in building and maintaining network infrastructure, which directly impacts pricing.
2. Taxes and levies
Government-imposed taxes on telecom services significantly contribute to the high cost of data.
3. Limited market competition
MTN’s dominance in the market, coupled with the absence of strong competitors, limits the downward pressure on prices.
4. Exchange rate and import costs
The depreciation of the Ghanaian cedi raises the cost of importing telecom equipment, a burden often passed on to consumers.
READ MORE: You're not among the best 2,000 defenders in the world- Sammy Kuffour jabs Carragher
Telecom companies’ perspectives
MTN Ghana maintains that its pricing reflects operational costs and the quality of services provided.
AirtelTigo and Vodafone Ghana have introduced competitive data bundles, but sustaining these low rates remains a challenge.
Some telecom operators argue that drastic price reductions could compromise network quality and hinder expansion efforts.
Government and regulatory efforts
The National Communications Authority (NCA) has implemented measures to regulate pricing and foster competition.
Policies like the Significant Market Power (SMP) initiative aimed to level the playing field, but their effectiveness remains debatable.
Advocates continue to call for reduced taxes on internet services to alleviate costs for consumers.
How are Ghanaians managing high data costs?
Many users opt for “midnight bundles” or rely on Wi-Fi hotspots to minimise expenses.
READ MORE: 16-year-old footballer sodomised by coach dies, mother demands justice [Video]
Social media-specific bundles (e.g., WhatsApp or Facebook packs) are popular alternatives to full data plans.
Public Wi-Fi initiatives in universities and business districts are expanding, though coverage remains limited.
Is a price reduction on the horizon?
With global advocacy for affordable internet as a human right, Ghana could see lower prices if competition intensifies and government policies evolve.
The introduction of 5G technology may influence pricing—either reducing costs through improved efficiency or increasing them due to infrastructure investments.
Growing pressure from consumers and advocacy groups may compel telecom companies to offer more affordable data packages.
Read Full Story




















Facebook
Twitter
Pinterest
Instagram
Google+
YouTube
LinkedIn
RSS